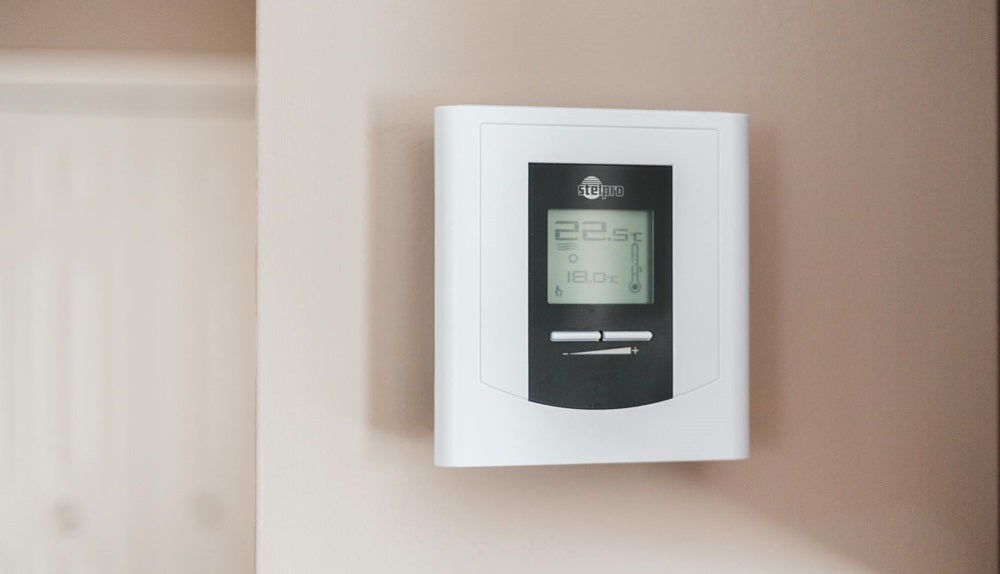
Thermostats play a huge role in the efficiency and effectiveness of the HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning) systems of millions of homes and offices. However, behind the scenes of every well-ventilated and cooled building is a complex network of thermostat wires, religiously guided by the thermostat wiring color code.
This colony of color-coded wiring ensures communication between the thermostat and the corresponding HVAC system. Understanding this color code is crucial to the proper installation of a new thermostat or the troubleshooting of your building's heating issues.
Thermostat Wiring Color Code Explained
So many different thermostat wire configurations exist for thermostat installations depending on the type of system it is for (e.g., traditional heating/cooling, heat pump, etc.), as well as the thermostat model you have.
While the wire configuration for thermostats might vary from one system or model to another, some general thermostat wiring color codes apply to virtually every system.
Below is a list of the most common thermostat wiring color codes used for thermostat wiring:
Power (R-Wire)
Many thermostat installers would argue that the power or R-Wire is perhaps the most important wire in a thermostat connection system as it helps to supply at least 24V of power to the thermostat. This wire is Red in color and connects to the R terminal on the thermostat, which then connects to the transformer of your HVAC system.
There are typically various versions of the Red/Power wire depending on the specific function of the wire. These are:
- Power Supply (R-Wire): The thermostat wire labeled R supplies 24V of power to the thermostat to ensure the device functions properly. Any HVAC system with only one R-wire typically has only one transformer controlling both cooling and heating within the system.
- Heating Power (RH-Wire): If the red wire in your thermostat/HVAC system is labeled as RH, then this wire comes from the heating system within the HVAC system.
- Cooling Power (RC-Wire): Red wires labeled as RC help to connect the thermostat to the cooling system in your HVAC system.
Note:Systems with two transformers typically have separate RH and RC wires since they need two power wires to connect the cooling transformer to the thermostat and the heating transformer of the HVAC system.
In older systems, the two terminals on the thermostat base are typically connected using a jumper wire. This connection is used to connect the RC and RH terminals in a single transformer HVAC system.
Common (C-Wire)
In most HVAC thermostat connections, the common wire or C-wire is usually blue or black, and it is used to provide a continuous power source for the thermostats. The C-wire is especially important in smart thermostats as they typically feature extra functions like Wi-Fi connectivity, LED backlighting, touchscreen power, and programmable settings.
The C-wire helps to connect the C-terminal on the thermostat to the Common terminal of your HVAC system. Not every HVAC system comes with a C-terminal for a C-wire connection.
You must take note of this during the installation of your HVAC system, especially if you intend to upgrade to a smart thermostat in the future. Also, it is important to use a thermostat cable that comes with a C-wire.
Heat (W-Wire)
The heat wire is also known as the W-wire, and in most thermostats and HVAC systems, it is typically white. The W-wire helps your thermostat control your heating system by connecting the W terminal on your thermostat to the heating equipment in your HVAC system (e.g., furnace, boiler, etc.).
The heat wire found in conventional heating systems is usually labeled as W or W1, and this simply connects to the equivalent terminal in your thermostat.
If your HVAC system utilizes an air conditioner or heat pump with auxiliary heating, then the AUX/AUX1 wire of these devices will be inserted into the W1 or AUX terminal on the thermostat.
Note: AUX wires do not have any universal color to help discern them from other wires in a thermostat-HVAC connection.
Two-Stage Heating (W2-Wire)
If your HVAC system uses a two-stage heating system, then it will likely come with a W2 wire that helps control stage 2 of heating in a conventional furnace, auxiliary heat or an electric furnace. Auxiliary heat is known as second-stage heat, as it typically kicks in when the first-stage heating system (typically heat pumps) struggles to keep your building warm enough for comfort.
The wires and terminals for second-stage heating are usually labeled as W2, AUX2, E, E/EM, and E/AUX. The wires used for second-stage heating are usually white, brown, or any other color chosen by the manufacturer. If your thermostat does not have an AUX2 terminal, you can simply put the AUX2 wire into the W2 terminal on your thermostat.
Air Conditioning (Y-Wire)
The air conditioning wire is also known as the Y-wire, and it helps to control the air conditioning in a building. The Y-wire helps to connect the Y-terminal of the thermostat to the compressor of the air conditioning unit in an HVAC system.
The Y-wire in most thermostat-HVAC connections is usually yellow or light blue in color. Just like it is in HVAC systems with two-stage heating, HVAC systems with two-stage cooling typically have Y1 and Y2 wires.
Fan (G-Wire)
The Green or G-wire is a primary wire in every thermostat as it helps to control the fan that circulates air in an HVAC system. This wire is typically labeled G and connects the G terminal of a thermostat to the blower motor in your specific HVAC system. Essentially, the G-wire is in charge of making sure the system kicks in when you select "Auto" or "On" on your thermostat.
Additional Wires and Terminals
Depending on the complexity of your system, you may encounter additional wires and terminals that suit your system's use case.
Below are some of these additional color codes and wires:
Emergency Heat (O or E-Terminal): Some HVAC systems use an orange wire to indicate the emergency heat wire. This wire is typically labeled O or E, and it connects to similarly labeled terminals. The O/E-wire is typically used to connect auxiliary heat, such as heating elements, in some heat pump systems.
Reversing Valve (O or B-Terminal): In heat pump systems, the orange wire, typically labeled as O or B-wire, connects to the O or B terminal to control the reversing valve. The reversing valve helps to change the direction of refrigerant flow for heating or cooling.
The thermostat wiring color code listed and described above does not represent the entirety of the color combinations and wire types found in every thermostat and HVAC system, but every thermostat is likely to contain some or all of them.
Exploring Specific Systems in Terms of Thermostat Installation & Troubleshooting
It is important that you consult the specific thermostat wiring diagram and installation guide of your thermostat for accurate wiring information.
Below is a breakdown of thermostat wiring color codes for common HVAC systems:
- Traditional Heating/Cooling Systems: These types of HVAC systems typically use a 4-wire or 5-wire setup, usually a combination of R, W, Y, G, and sometimes, C.
- Heat Pump Systems: Heat pump thermostats usually use additional wires like Orange (O/B) for the reversing valve. Some heat pump systems may still require a common wire (C) for smart thermostat features.
Two common thermostat brands include Honeywell Thermostats and Sensi Thermostats.
Now that you understand the common thermostat wiring color code for different HVAC systems, you can carry out DIY projects involving thermostats. However, we still recommend that you consult with professional installers to help set up the HVAC thermostat connection in your home.
All Security Equipment is a one-stop shop for all things relating to home security, including accessories like high-quality thermostat cables and access control accessories.
Contact us today to learn how we can help with your thermostat cables.